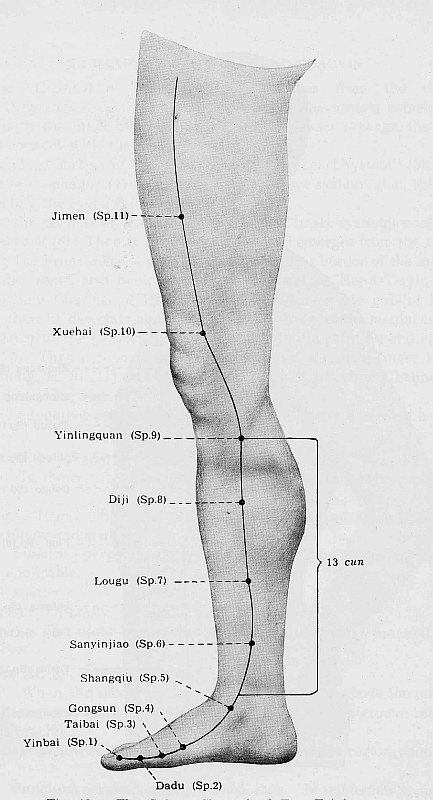
Spleen Channel

Sp 1 Yinbai** Jing-Well Point
FUNCTIONS: Tonify Spleen, regulate menstruation, calm the Spirit.
Strengthen Spleen function of holding Xue- hence menorrhagia (moxa). Bleed
for manic depression. Moxa for excess dreaming or startled sleep.
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal distension.[1] Bleeding
of the digestive tract.[2] Abdominal
pain.[2]
2. Abnormal uterine bleeding.[1]
3. Mental disorders.[1] Dream disturbed
sleep.[1] Convulsion.[1]
Mental diseases.[2]
LOCATION: On the medial side of the big toe, about 0.1 cun posterior
to the corner of the nail.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 3 mm.[1]
Sp2 Dadu** Ying-Spring Point
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal distension.[1] Gastric
pain.[1] Diarrhea.[2]
Stomache ache.[2]
2. Febrile diseases with anhydrosis.[1]
Fever.[2]
3. Apoplectic coma.[2]
4. Edema of the limbs.[2]
LOCATION: On the medial side of the big toe, distal and inferior to the
1st metatarsodigistal joint, at the junction of the red and white skin.
METHOD: Perpenducularly 3-5 mm.[1]
Sp 3 Taibai* Shu- stream and Yuan- Source
Point
FUNCTIONS: Eliminate both internal and external dampness and to tonify
Spleen.
1. Gastric pain.[1] Abdominal distension.[1]
Dysentery.[1] Constipation.[1]
Vomiting.[1] Diarrhea.[1]
Acute gastroenteritis.[2]
2. Edema.[2] Sluggishness.[1]
Beriberi.[1]
3. Headache.[2]
LOCATION: Proximal and inferior to the head of the 1st metatarsal bone,
at the junction of the red and white skin.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8 mm.[1]
Sp 4 Gongsun** Luo- Connecting Point

FUNCTIONS: Regulate the function of Spleen and Stomach. To
invigorate Chong Mai. Better than Sp3 for pain.
INDICATIONS
1. Vomiting.[1]Gastric pain.[1]
Borborygmus.[1] Abdominal pain.[1]
Diarrhea.[1] Dysentery.[1]
Stomach ache.[2] Acute and chronic
enteritis.[2]
2. Foot and ankle pain.[2]
3. Endometritis.[2] Irregular menstruation.
[2]
LOCATION: In the depression distal and inferior to the base of the 1st
metatarsal bone, at the junction of the red and white skin.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Sp 5 Shangqiu** Jing- River Point
FUNCTIONS: Strengthen Spleen and Stomach and remove Damp stagnation.
Good as a general Jing point for joint pain.
INDICATIONS
1. Borborygmus.[1] Abdominal distension.[1]
Constipation.[1] Diarrhea.[1]
Gastritis.[2] Enteritis.[2]
Indigestion.[2]
2. Pain in the foot and ankle joint. [1]Diseases
of the ankle and surrounding soft tissues.[1]
3. Edema.[2]
4. Stiffness and pain of the tongue.[1]
5. Beriberi.[2]
LOCATION: In the depression distal and inferior to the medial malleolus,
midway between the tuberosity of the navicular bone and the tip of the medial
malleolus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 5-8 mm.[1]
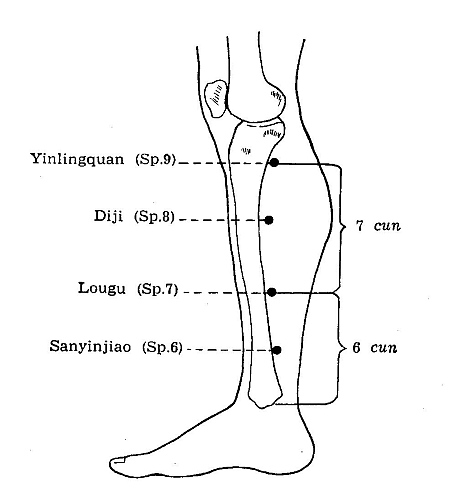
Sp 6 Sanjinjiao**
FUNCTIONS: Reinforce Spleen to eliminate Damp, promote the function
of Stomach and Spleen, invigorate the circulation of Qi and Blood, clear Jingluo.
Strengthens Liver free-going function. Benefits Kidney. Much used for insomnia.
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal distension.[1] Borborygmus.[1]
Loose stools with undigested food.[1]
Hernia.[1] Pain of the abdomen.[2]
Diarrhea.[2]
2. Irregular menstruation.[1] Uterine
bleeding.[1] Leukorrhea.[1]
Prolapse of uterus.[1] Amenorrhea.[1]
Sterility.[1] Difficult labour.[1]
Seminal emission.[1] Pain of the external
genitalia.[1] Dysuria.[1]
Enuresis.[1] Incontinence.[2]
Diseases of the reproductive system.[2]
3 . Muscular atrophy.[1] Motor impairment
and paralysis and pain of the lower extremities.[1]
Hemiplegia.[2]
4. Neurodermatitis.[2] Eczema.[2]
Urticaria.[2]
5. Neurasthenia.[2] Insomnia.[1]
LOCATION: 3 cun directly above the tip of the medial malleolus, on the
posterior border of the tibia, on the line drawn from the medial malleolus to
Yinlingquan- Sp 9.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular13-25 mm.[1]
Sp 7 Lougu*
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal distension.[1] Borborygmus.[1]
2. Cold, numbness and paralysis of the knee and leg.[1]
Paralysis of lower limb.[2]
3. Urinary tract infection.[2]
LOCATION: 6 cun above the tip of the medial malleolus, 3 cun above Sanjinjiao-Sp
6.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm..[1]
Sp 8 Diji** Xi- Cleft Point
FUNCTIONS: Regulates Blood, regulates uterus. Menstrual problems,
dysmenorrhea.
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal distension.[1] Anorexia.[1]
Dysentery.[1]
2. Irregular menstruation.[1] Dysuria.[1]
Seminal emission.[1] Abnormal uterine
bleeding.[2] Dysmenorrhea.[2]
Nocturnal emissions.[2]
3. Edema.[1]
LOCATION: 3 cun below the medial condyle of the tibia, on the line connecting
Yinglingquan- Sp 9 and the medial malleolus.[1]
METHOD Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Sp 9 Yinlingquan** He-Sea Point
FUNCTIONS: Dispels Damp stagnation, adjust lower Jiao. Eliminate Damp-Heat
from lower Jiao.
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal distension.[1] Diarrhea.[1]
Ascites.[2] Enteritis.[2]
Dysentery.[2] Edema.[1]
2. Incontinence of urine.[1]
Dysuria.[1] Pain of the external genitalia.[1]
Seminal emission.[1] Retention of
urine.[2] Urinary tract infection.[2]
Irregular menstruation.[2] Nocturnal
emissions.[2] Impotence.[2]
Nephritis.[2]
3. Pain of the knee.[1]
4. Jaundice.[1]
5. Beriberi.[2]
LOCATION: On the lower border of the medial condyle of the tivia, in
the depression between the posterior border of the tibia and the gastrocnemius
muscle.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Sp 10 Xuehai**

FUNCTIONS: Dispel Heat from Blood, regulate circulation of nourishing
Jing,Qi and Blood. Dispel Wind.
INDICATIONS:
1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Dysmenorrhea.[1]
Amenorrhea.[1] Abnormal uterine bleeding.[1]
2. Eczema.[1] Uticaria.[1]
Pruritis.[2] Neurodermatitis.[2]
Anemia.[2]
3. Pain in the medial aspect of the thigh.[1]
LOCATION: When the knee is flexed, the point is 2 cun above the mediosuperior
border of the patella, on the bulge of the medial portion of the quadriceps
femoris muscle. Another way to locate this point is to cup your right
palm to the patient's left knee, with the thumb on ths medial side and the other
four finger directed proximally. The point is where the tip of your thumb rests.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 18-30 mm.[1]
Sp 11 Jimen*
INDICATIONS
1. Enuresis.[1] Retention of
urine.[1] Pain and swelling of the
inguinal region.[1] Urethritis. Inguinal
lymphadenitis.[2]
LOCATION: 6 cun above Xuehai-Sp 10, on the line drawn from Xuehai to
Chongmen- Sp 12.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
Sp 12 Chongmen*

INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal pain.[1] Hernia.[1]
2. Retention of urine.[1] Endometritis.[2]
Orchitis.[2]
LOCATION: Superior to the lateral end of the inguinal groove, on the
lateral side of the femoral artery, at the level of the upper border of symphysis
pubis, 3.5 cun lateral to Qugu- Ren 2.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Sp 13 Fushe*
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal pain.[1] Mass in the
abdomen.[1] Pain of hernia.[1]
Appendicitis.[2] Inguinal lymphadenitis.[2]
Adenitis.[2]
LOCATION: 0.7 cun above Chongmen- Sp 12, 4 cun lateral to the Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 18-25 mm.[1]
Sp 14 Fujie*
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal pain around the umbilical region.[1]
Hernia.[1] Diarrhea.[1]
LOCATION: 3 cun above Fushe- Sp 13, 1.3 cun below Daheng- Sp 15, on the
lateral side of the rectus abdominis muscle.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm..[1]
Sp 15 Daheng**

INDICATIONS
1. Constipation.[1] Abdominal distension.[2]
Dysentery.[1] Pain in the lower abdomen.[1]
Abdominal distension.[2] Diarrhea.[2]
Intestinal paralysis.[2] Parasitic
worms in the intestines.[2]
LOCATION: 4 cun lateral to the centre of the umbilicus, on the mammilary
line, lateral to the rectus abdominis muscle.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Sp 16 Fuai*
INDICATIONS
1. Indigestion.[1] Constipation.[1]
Dysentery.[1]Abdominal pain.[1]
Pain in the region of the umbilicus.[2]
LOCATION: 3 cun above Daheng- Sp 15.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Sp 17 Shidou*
INDICATIONS
1. Sensation of fullness and pain in the chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2] Ascites.[2]
Gastritis.[2]
2. Retention of urine.[2]
LOCATION: 6 cun lateral to the Ren Channel, or 2 cun lateral to the mammillary
line, in the 5th intercostal space.[1]
METHOD: Puncture obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
Sp 18 Tianxi*
INDICATIONS
1. Sensation of fullness and pain in the chest.[1]
Mastitis[1,2] Lactation deficency.[1]
2. Cough.[1] Bronchitis.[2]
Asthma.[2]
3. Hiccough.[2]
LOCATION: 2 cun lateral to the nipple, in the 4th intercostal space.[1]
METHOD Puncture obliquely 10-13 mm, or apply moxa stick for 5-10
minutes.[1]
Sp 19 Xiongxiang*
INDICATIONS
1. Sensation of fullness and pain in the chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
2. Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
LOCATION: One rib above Tianxi-Sp 18, in the 3rd intercostal space, 6
cun lateral to the Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD Puncture obliqely 10-13 mm.[1]
.
Sp 20 Zhourong*
INDICATIONS
1. Sensation of fullness in the chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
2. Cough.[1] Pleurisy.[2]
Pulmonary emphysema[2] Bronchiectasis.[2]
LOCATION: One rib above Xiongxiang-Sp 19, directly below Zhongfu-Lu 1
and Yunmen- Lu 2, in the second intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the Ren
Channel.[1]
METHOD: Puncture obliquely 10-13 mm.[1]
Sp 21 Dabao* Major Luo- Connecting point of the
Spleen
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
General aching and weakness.[1] Intercostal
neuralgia.[2] General body
soreness.[2]
2. Asthma.[1]
LOCATION: On the mid-axillary line, 6 cun below the axilla, midway between
the axilla and the free end of the 11th rib.[1]
METHOD: Puncture obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
[1] Essentials of Chinese Acupuncture. 1980 Beijing College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing College of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Foreign Languages Press Beijing
[2] Acupuncture: A comprehensive Text; Beijing