
Small Intestine Channel

SI 1 Shaoze** Jing- Well Point
FUNCTIONS: Dispel Wind-Heat, promote the flow of mild. Good for neckache.
INDICATIONS
1.Febrile diseases.[1] Sore throat.[1]
2. Loss of consciousness.[1] Headache.[2]
3. Lactation deficiency.[1] Mastitis.[2]
4. Cloudiness of cornea.[1] Pterygium.[2]
LOCATION: On the ulnar side of the little finger, about 0.1 cun posterior
to the corner of the nail.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 3 mm.[1]
SI 2 Qiangu* Ying- Spring Point
INDICATIONS
1. Numbness of fingers.[1]
2. Febrile diseases.[1]
3. Mastitis.[2]
4. Tinnitus.[2] Congested throat.[2]
5. Pannus (newly formed superficial vascular tissue over the cornea).[2]
LOCATION: When a loose fist is made, the point is distal to the
metacarpophalangeal joint, at the junction of the red and white skin.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 5-8 mm.[1]
SI 3 Houxi **
FUNCTIONS: Clear the mind, eliminate Wind-Heat, clears Du Mai, relax
tendons and muscles. Treat malaria.
INDICATIONS
1. Neck rigidity.[1] Headache.[1]
Contracture and twitching of the elbow, arm and fingers.[1]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2] Low back
pain.[2]
2. Epilepsy.[1] Seizures.[2]
Psychosis.[2] Hysteria.[2]
3. Congestion of the eye.[1]
4. Febrile diseases.[1] Malaria.[1]
Night sweating.[1]
5. Deafness.[1] Deaf-mutism.[2]
LOCATION: When a loose fist is made, the point is proximal to the head
of the 5th metacarpal bone on the ulnar side, in the depression at the junction
of the red and white skin.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-18 mm.[1]
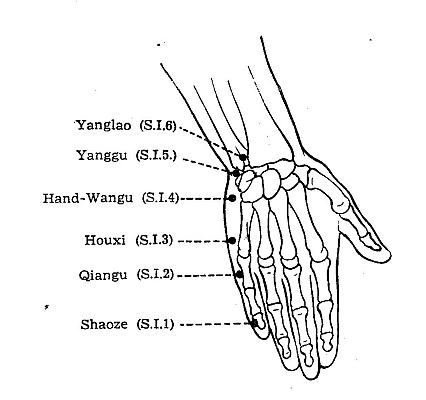
SI 4 Hand - Wangu** Shu- Stream Point
FUNCTIONS: Invigorate Tai Yang, disperse Damp-Heat from Small Intestine.
For cholecystitis jaundice, hypochondriac pain.
INDICATIONS
1. Headache.[1] Neck rigidity.[1]
Arthritis of the wrist, elbow and fingers.[2]
2. Pain in the hypochondriac region.[1]
Gastritis.[2] Cholecystitis.[2]
3. Cloudiness of cornea.[1] Jaundice.[1]
4. Tinnitus.[2]
5. Febrile diseases.[1]
6. Diabetes.[2]
LOCATION: On the ulnar side of the palm, in the depression beween the
base of the
5th metacarpal bone and the triquetral bone.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
SI 5 Yanggu* Jing- River Point
FUNCTIONS: Regulate Qi of Small Intestine. Good for Damp-Heat in knees
swollen, painful, hot.
INDICATIONS
1. Swelling of the neck and submandibular region.[1]
Pain in the wrist.[1] Pain in the
lateral aspect of the arm.[1]
2. Febrile diseases.[1]
3. Deafness.[2] Tinnitus.[2]
4. Insanity.[2]
5. Parotitis.[2]
LOCATION: On the ulnar side of the wrist, in the depression between the
styloid process of the ulna and the triquetral bone.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-10 mm.[1]
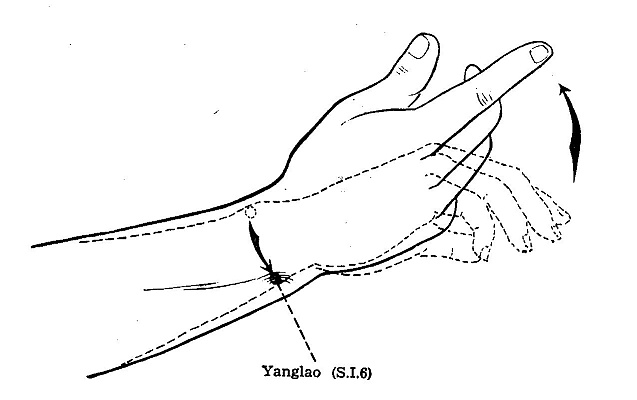
SI 6 Yanglao** Xi- Cleft Point
FUNCTIONS: Relax tendons, clears Jingluo, brighten the eyes.
INDICATIONS
1. Blurring of vision.[1] Eye diseases.[2]
2. Aching of the shoulder, back, elbow and arm.[1]
Arthritis of the upper limb.[2] Pain
in the shoulder and back.[2] Hemiplegia.[2]Stiff
neck.[2] Low back pain.[2]
Pain of hernia.[2]
LOCATION: Dorsal to the head of the ulna. When the palm faces the chest,
the point is in the bony cleft on the radial side of the styoid process of the
ulna.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
SI 7 Zhizheng* Luo- Connecting Point
INDICATIONS
1. Neck rigidity.[1,2] Contracture
and twitching of elbow.[2] Pain
in fingers.[2] Pain of the elbow or
arm.[2]
2. Mental disorders.[2]
3. Febrile diseases.[2]
4. Neurasthenia.[2]
LOCATION: 5 cun proximal to the wrist, on the line joining Yanggu SI
5, and Xiaohai- SI 8.[1]
METHOD Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
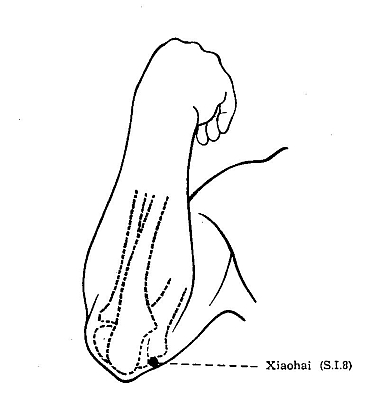
SI 8 Xiaohai* He- Sea Point

INDICATIONS
1. Swelling of the cheek.[1] Pain
in the nape and the lateroposterior, aspect of the shoulder and arm.[1,2]
Neuralgia or paralysis of the ulmar nerve.[1]
Chorea = Muscle twitching.[2]
2. Epilepsy.[1] Seizures.[2]
Psychosis.[2]
LOCATION: Between the olecranon of the ulna and the medial epcondyle
of the humerus. The point is located with the elbow flexed.[1]
METHOD Perpendicular 8-18 mm.[1]
SI 9 Jianshen**

FUNCTIONS: Shoulder problems.
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the scapular region.[1]
Pain and motor impairment of the hand and arm.[1]
Diseases of the shoulder and shoulder joint.[2]
Paralysis of the upper limb.[2]
2. Excessive perspiration in the arm pits.[2]
LOCATION: Posterior and inferior to the shoulder joint. When the arm
is adducted, the point is 1 cun above the posterior end of the axillary fold.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
SI 10 Naoshu**
FUNCTIONS: Shoulder problems.
INDICATIONS
1. Pain and weakness of the shoulder and arm.[12]
Hemiplegia.[2]
2. Hypertension.[2]
3. Excessive sweating.[2]
LOCATION: When the arm is adducted, the point is directly above
Jianshen SI 9, in the depression inferior and lateral to the scapular spine.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-25 mm.[1]
SI 11 Tianzong**
FUNCTIONS: Disperse fullness from chest, eliminate stagnation of Qi
from hypochondrium, treat shoulder.
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the scapular region.[1,2]
Pain in the lateroposterior aspect of the elbow and arm.[1]
Pain in the shoulder.[2] Pain in the
upper arm.[2]
LOCATION: In the infrascapular fossa, at the junction of the upper
and middle third of the distance between the lower border of the scapular spine
and the inferior angle of the scapular.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 13-25 mm.[1]
SI 12 Bingfeng*
FUNCTIONS: Shoulder problems
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the scapular region.[1,2]
Numbness and aching of the upper extremities.[1]
Inflammation of the supra spinatus tendon.[2]
LOCATION: In the centre of the suprascapular fossa, directly above Tiansong
SI 11. When the arm is lifted, the point is at the site of the depression.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-18 mm.[1]
SI 13 Quyuan**
INDICATIONS
1. Pain and stiffness of the scapular region.[1]
Inflammation of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle.[2]
Diseases of the soft tissues of the shoulder joint.[2]
LOCATION: On the medial extremity of the suprascapular fossa, about midway
between Naoshu- SI 10 and the spinous process of the 2nd thoracic vertebra.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
SI 14 Jianwaishu*
FUNCTIONS: Shoulder problems
INDICATIONS
1. Aching and pain of the shoulder and back.[1,2]
Rigidity of neck.[1]
LOCATION: 3 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of
the 1st thoracic vertebra Taodao Du 13, on the vertical line drawn from the
verterbral border of the scapula.[1]
METHOD: Puncture obliquely 8-15 mm.[1
SI 15 Jianzhongshu**
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the shoulder and back.[1,2]
Stiff neck.[2]
2. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1,2]
Bronchitis.[2] Bronchiectasis.[2]
Chronic dilation of bronchii.[2]
LOCATION: 2 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of
the 7th cervical vertebra, Dazhui- Du14.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-15 mm.[1]
SI 16 Tianchuang*
INDICATIONS
1. Stiffness and pain of neck.[1,2]
2. Deafness.[1,2] Tinnitus.[1,2]
3. Sore throat.[1,2]
4. Goiter.[2]
LOCATION: In the lateral aspect of the neck, on the posterior border
of the sternocleidomastoideus, posterosuperior to Neck Futu- LI 18.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 15-20 mm.[1]
SI 17 Tianrong**
FUNCTIONS: Tonsillitis, sore throat.
INDICATIONS
1. Foreign body sensation in throat.[1]
Sw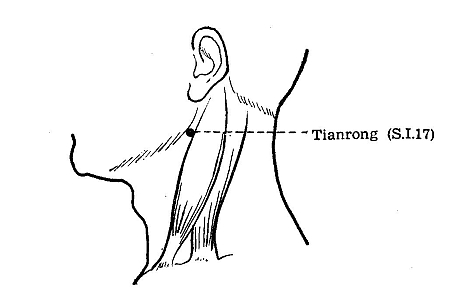 elling of cheek.[1]
Distension and soreness of the neck.[2]
elling of cheek.[1]
Distension and soreness of the neck.[2]
2. Deafness.[1] Tinnitus.[1]
3. Sore throat.[1] Tonsillitis.[2]
Pharyngitis.[2] Asthma.[2]
LOCATION: Posterior to the angle of mandible, in the depression
on the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1].
SI 18 Quanliao*

FUNCTIONS: Dispel Wind, relieve pain, sedative function.
INDICATIONS
1. Facial paralysis.[1,2] Twitching
of eyelids.[1] Trigeminal neuralgia.[2]
Spasm of the facial muscles.[2]
2. Yellowish sclera.[1]
3. Toothache.[1]
LOCATION: Directly below the outer canthus, in the depression on the
lower border of zygoma.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1]
SI 19 Tinggong*
FUNCTIONS: Clears Jingluo; to ease the ears.
INDICATIONS
1. Deafness.[1,2] Tinnitus.[1,2]
Otorrhea.[1] Deaf mutism.[2]
Otitis media.[2] Inflammation of the
external ear canal.[2]
LOCATION: Between the tragus and the mandibular joint, where a depression
is formed when the mouth is slightly open.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-25 mm.[1]
[1] Essentials of Chinese Acupuncture Shanghai
[2] Acupuncture A comprehensive Text Beijing