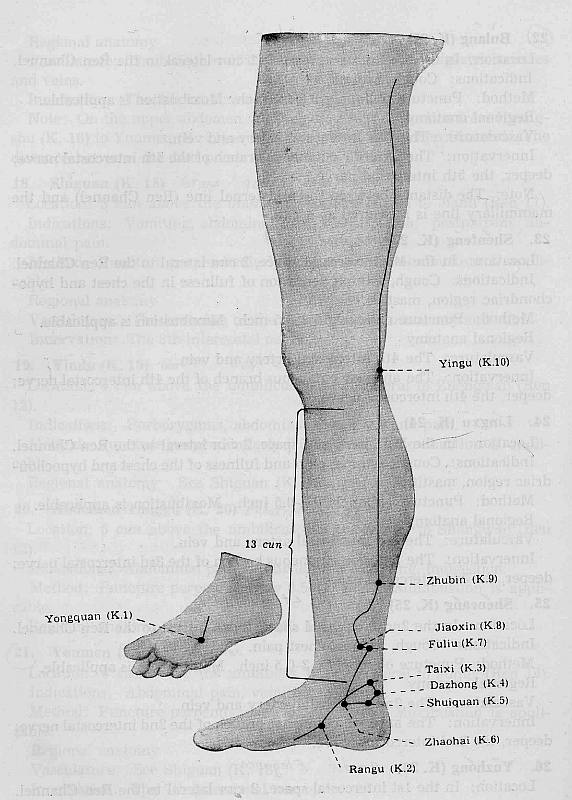
Kidney Channel

Ki 1 Yongquan** Jing- Well Point
FUNCTIONS: Tonify Yin, pacify Fire, calm the Heart
and Spirit, rendering the effect of resuscitation. Emergency
point (bled)
Opens sensory orifices
INDICATIONS
1 . Headache at vertex.[1] Hypertension.[2]
2 . Dizziness.[1] Infantile convulsion.[1]
Loss of consciousness.[1] Insomnia.[2]
Stroke.[2] Seizures.[2]
Psychosis.[2] Mental illness.[2]
3. Sore throat.[1] Dryness of the
tongue.[1] Aphonia.[1]
4. Paralysis of the legs.[2] Feverish
sensation of the sole.[1]
4. Dyschezia (Painful or difficult bowel movements).[2]
5. Blurring of vision.[1]
6. Dysuria.[1]
7. Shock.[2] Heat exhaustion.[2]
LOCATION: In the depression appearing on the sole when the
foot is in plantar flexion, approximately at the junction of the anterior and
middle third of the sole.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 2 Rangu** Ying- Spring Point
FUNCTIONS: Pacify Fire, ease the throat, strengthen
Yin Qiao Mai. Eliminates Heat to cool the Blood.
INDICATIONS
 1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Pruritus
vulvae.[1] Prolapse of uterus.[1]
Seminal emission.[1] Cystitis.[2]
1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Pruritus
vulvae.[1] Prolapse of uterus.[1]
Seminal emission.[1] Cystitis.[2]
2. Hemoptysis.[1] Pharyngitis.[2]
3. Diarrhea.[1]
4. Swelling and pain of the dorsum of foot.[1]
5. Diabetes.[2]
6. Tetanus.[2]
LOCATION: Anterior and inferior to the medial malleolus, in
the depression on the lower border of the tuberosity of the navicular bone.
[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8 mm.[1]
 Ki
3 Taixi** Shu-Stream and Yuan- Source Point
Ki
3 Taixi** Shu-Stream and Yuan- Source Point
FUNCTIONS: Tonify Qi of Ki, pacify Empty Fire, promote
the function of Uterus, strengthen the lower back and knees. Much used to tonify
Kidney.
INDICATIONS
1. Toothache.[1] Sore throat.[1]
Hemoptysis.[1] Asthma.[1]
Chronic laryngitis.[2] Tinnitus.[2]
Emphysema.[2]
2. Irregular menstruation.[1] Seminal
emission.[1] Impotence.[1]
Frequency of micturition.[1] Nephritis.[2]
Cystitis.[2] Spermatorrhea.[2]
Enuresis.[2]
3. Pain in the lower back.[1] Paralysis
of lower limb (up-turned foot).[2]
Pain in the sole of foot.[2]
4. Deafness.[1]
5. Insomnia.[1] Neurasthenia.[2]
6. Alopecia.[2]
LOCATION: In the depression between the medial malleolus, in
the depression on the lower border of the tuberosity of the navicular bone.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8 mm.[1]
Ki 4 Dazhong* Luo- Connecting Point
INDICATIONS
1. Asthma.[1] Hemoptysis.[1]
Soreness in pharynx.[2]
2 . Dysuria.[1,2]
3 . Pain in heel.[1,2] Stiffness of
the lumbosacral region.[1]
4. Neurasthenia.[2] Hysteria.[2]
5. Malaria.[2]
LOCATION: Posterior and inferior to the medial malliolus, in
the depression medial to the attachment of tendocalcaneus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8 mm.[1]
 Ki
5 Shuiquan* Xi- Cleft Point
Ki
5 Shuiquan* Xi- Cleft Point
INDICATIONS
1. Irregular menstuation.[1] Dysmenorrhea.[1]
Amenorrhea. Prolapse of uterus.[1]
2. Blurring of vision.[1] Myopia.[2]
3. Dysuria.[1]
LOCATION: 1 cun directly below Taixi (Ki 3), in the depression
anterior and
superior to the medial side of the tuberosity of the calcaneum.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 10 mm.[1]
Ki 6 Zhaohai**
FUNCTIONS: Eliminate Heat, calm the Spirit, promote the function
of the uterus, clear Yin Qiao Mai. Together with Lieque(Lu 7) tonifies Yin,
eases the throat. Used to tonify Lu Yin in chronic cough.
INDICATIONS
1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Prolapse
of uterus.[1] Pruritus vulvae.[1]
Frequency of micturition.[1]
2. Seizures.[1] Insomnia.[1]
Neurasthenia.[2] Psychosis.[2]
3. Sore throat.[1] Pharyngitis.[2]
Tonsillitis.[2]
4. Hernia.[1]
LOCATION: 1 cun below the medial malleollus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 7 Fuliu** Jing- River Point
FUNCTIONS: Regulate Ki Qi, eliminate Damp-Heat, tonify
back. Much used for sweating in combination with Yinxi(He 6).
INDICATIONS
1. Diarrhea.[1] Borborygmus.[1]
Abdominal distension.[1]
2. Swelling of leg.[1] Edema.[1]
Muscular atrophy.[1] Weakness and
paralysis of foot.[1] Low back pain.[2]
3. Nephritis.[2] Orchitis.[2]
Functional uterine bleeding.[2] Urinary
tract infection.[2] Leukorrhea.[2]
4. Night sweating.[1] Spontaneous
sweating.[1]
LOCATION: 2 cun directly above Taixi (Ki 3), on the anterior
border of tendo calcaneus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 8 Jiaoxin*
INDICATIONS
1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Abnormal
uterine bleeding.[1] Prolapse of uterus.[1]
Pain and swelling of testis.[1]
2. Diarrhea.[1] Constipation.[1]
3. Pain on the medial aspect of lower limb.[2]
4. Retention of urine.[2]
LOCATION: 2 cun above Taixi- Ki 3, 0.5 cun anterior to Fuliu-
Ki 7, posterior to the medial border of tibia.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 10 mm.[1]
Ki 9 Zhubin**
FUNCTIONS: Tonify Di Qi, calm the mind, tonify Yin Wei
Mai. Excellent in conjunction with Yin Wei Mai.
INDICATIONS
1. Mental disorders.[1] Seizures.[2]
Psychosis.[2]
2 . Pain in the medial aspect of the leg.[1]
Spasm of the gastrocnemius muscle.[2]
3. Nephritis.[2] Cystitis.[2]
Orchitis. [2]Pelvic inflammatory disease.[2]
LOCATION: On the line drawn from Taixi- Ki3 to Yingu- Ki10,
at the lower end of the belly of the gastrocnemius in the medial aspect, about
5 cun above Taixi- Ki 3.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1]
Ki 10 Yingu* He-Sea Point
FUNCTIONS: Tonify Kidney, dispel Heat, regulate and soothe
lower jiao.
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the medial aspect of the thigh and knee.[1]
Arthritis of the knee.[2]
2. Impotence.[1] Abnormal uterine
bleeding.[1] Diseases of the urogential
system.[2]
3. Hernia.[1]
LOCATION: On the medial side of the popliteal fossa, level
with Weizhong (UB40), between the tendons of semitendinosis and semimembranosus
when the knee is flexed.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-25 mm.[1]
Ki 11 Henggu* 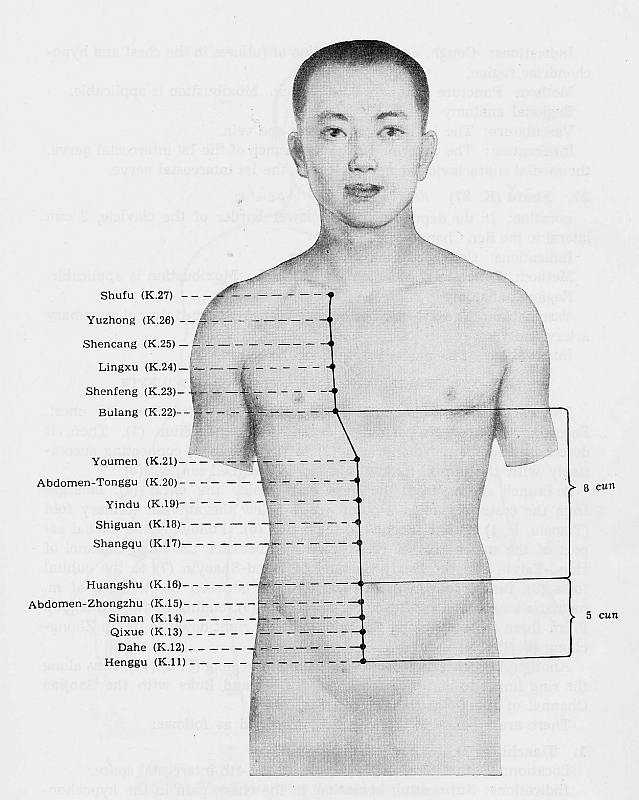
INDICATIONS
1. Impotence.[1] Spermatorrhea.[1]
Pain in the external genitalia.[1]
Retention of urine.[1] Urethritis.[2]
Incontinence of urine.[2] Uterine
bleeding.[1]
2. Hernia.[2]
LOCATION: 0.5 cun below the umbilicus, on the superior border
of symphysis pubis, 0.5 cun lateral to Qugu- Ren 2.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1]
Ki 12 Dahe** 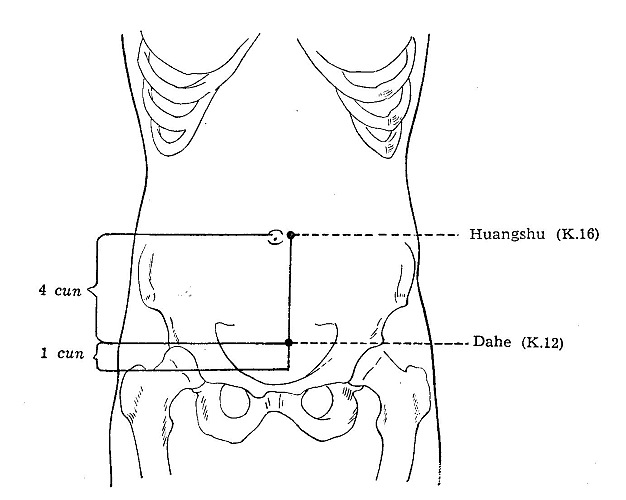
INDICATIONS
1. Leukorrhea.[1,2] Spermatorrhea.[1]
Neuralgia of the spermatic cord.[2]
Pain in the external genitalia.[1]
LOCATION: 4 cun below the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Zhongji-
Ren 3.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 13 Qixue*
INDICATIONS
1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Leukorrhea.[2]
Sterility.[2] Urinary tract infection.[2]
2. Diarrhea.[1]
LOCATION: 3 cun below the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Guanyuan-
Ren 4.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 14 Siman*
INDICATIONS
1 . Irregular menstruation.[1]
Uterine bleeding.[1] Postpartum abdominal
pain.[1] Leukorrhea.[2]
Sterility.[2] Urinary tract infection.
[2]
2. Diarrhea.[1]
LOCATION: 2 cun below the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Shimen-
Ren 5.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 15 Abdomen Zhongshu*
INDICATIONS
1. Lower abdominal pain.[1] Constipation.[1]
2. Irregular menstruation.[1]
3. Low back pain.[2]
LOCATION: 1 below the umbilicus, .5 cun lateral to Shimen-
Ren 5.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 16 Huangshu*
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal pain.[1]Vomiting.[1]
Abdominal distension.[1] Constipation.[1]
Stomach spasms.[2] Pain of hernia.[2]
Enteritis.[2] Habitual constipation.[2]
2. Hiccough.[2]
LOCATION: 0.5 cun lateral to the centre of the umbilicus. [1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 17 Shangqu*
INDICATIONS
1. Fullness of abdomen.[1] Diarrhea.[1]
Constipation.[1] Stomache-ache.[2]
Colic.[2] Peritonitis.[2]
LOCATION: 2 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Xiawan-
Ren10.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 18 Shiguan*
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal pain.[1] Constipation.[1]Vomiting.[1]
2. Hiccoughs.[2] Spasms of esophagus.[2]
3. Postpartum abdominal pain.[1]
LOCATION: 3 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Jianli-
Ren11.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 19 Yindu*
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal distension and pain.[1]
Borborygmus.[1]
2. Emphysema.[2] Pleurisy.[2]
3. Malaria.[2]
LOCATION: 4 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Zhongwan-
Ren12.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 20 Abdomen Tonggu*
INDICATIONS
1. Vomiting.[1] Abdominal
pain and distention.[1] Indigestion.[1]
Diarrhea.[2]
2. Stiff neck.[2] Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
3. Seizures.[2]
4. Palpiations.[2]
LOCATION: 5 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Shangwan
(Ren13).[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular13-25 mm.[1]
Ki 21 Youmen*
INDICATIONS
1. Abdominal pain.[1] Vomiting.[1]
Diarrhea.[1] Distended stomach.[2]
Stomach spasms.[2] Chronic gastritis.[2]
2. Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
LOCATION: 6 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to Juque-
Ren14.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-18 mm.[1]
Ki 22 Bulang*
INDICATIONS
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Pleurisy.[2] Rhinitis.[2]
Bronchitis.[2]
2. Gastritis.[2]
3. Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
LOCATION: In the 5th intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the
Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 23 Shenfeng*
INDICATIONS :
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Pleurisy.[2] Bronchitis.[2]
2. Mastitis.[1]
3 . Intercostal neuralgia.[2] Sensation
of fullness in the chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
LOCATION: In the 4th intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the
Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 24 Lingxu*
INDICATIONS
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Bronchitis.[2]
2. Pain and fullness of the chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
3. Mastitis.[1]
4. Vomiting.[2]
LOCATION: In the 3rd intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the
Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 25 Shencang*
FUNCTIONS: Cough, asthma from Ki-Xu.
INDICATIONS
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Bronchitis.[2]
2. Intercostal neuralgia.[2] Chest
pain.[1]
3. Vomiting.[2]
LOCATION: In the 2nd intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the
Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 26 Yuzhong*
INDICATIONS
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Bronchitis.[2]
2. Intercostal neuralgia.[2] Sensation
of fullness in the chest and hypochondriac region.[1]
3. Vomiting.[2]
LOCATION: In the 1st intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the
Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD: Obliqeuly 8-13 mm.[1]
Ki 27 Shufu*
INDICATIONS
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Bronchitis.[2]
2. Chest pain.[1]
3. Vomiting.[2] Abdominal distention.[2]
LOCATION: In the depression on the lower border of the clavicle,
2 cun lateral to the Ren Channel.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8 mm.[1]
[1] Essentials of Chinese Acupuncture Shanghai
[2] Acupuncture A comprehensive Text Beijing