
CV 1 Huiyin*
INDICATIONS
1. Pruritus vulvae.[1] Irregular
menstruation.[1] Seminal emission.[1]
Prostatitis.[2]
2. Retention of urine.[1] Enuresis.[1]
Urethritis.[2]
2. Mental disorders.[1]
3. Pain and swelling of the anus.[1]
4 . Revive from drowning.[2]
LOCATION: In the centre of the perineum. It is between the anus and the
scrotum in males and between the anus and the posterior labial commissure in
females. [1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-20 mm.[1]
CV 2 Qugu*
INDICATIONS
1. Seminal emission.[1]
Impotence.[1] Leukorrhea.[1]
Hernia.[1] Irregular menstruation.[2]
Orchitis.[2] Prolapsed uterus.[2]
2. Cystitis. Retention of urine.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, just above the
symphysis pubis.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-25 mm.[1]
CV 3 Zhongji** Front- Mu Point of the Urinary Bladder
FUNCTIONS: Regulate and promote the function of the uterus, regulate
lower Jiao, eliminate Damp-Heat. Assists in the transforming function of Qi.
INDICATIONS:
1. Enuresis.[1] Retention of
urine.[1] Frequency of micturition.[1]Nephritis.[2]
Urethritis.[2]
2. Irregular menstruation.[1]
Leukorrhea.[1] Seminal emission.[1]
Uterine bleeding.[1] Prolapse of uterus.[1]
Pain of the external genitalia.[1]
Pruritus vulvae.[1] Spermatorrhea.[1,2]
Impotence.[2] Premature ejaculation.[2]
Female sterility.[2] Pelveoperitonitis.[2]
Dysmenorrhea.[2]
3. Pain in the lower abdomen.[1]
4 . Sciatica.[2]
LOCATION: On the anterior midline, 4 cun below the umbilicus, 1 cun
above the upper border of symphysis pubis.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20 mm.[1]
CV 4 Guanyuan** Front- Mu Point of the Small Intestine
FUNCTIONS: Promote the function of the Ki, tonify Yuan Qi, regulate
menstrual flow. Much used for dysmenorrhoea. Restores Yang. Regulates Qi.
INDICATIONS
1. Enuresis.[1] Seminal
emission.[1] Frequent urination.[1]
Retention of urine.[1] Urinary tract
infection.[2] Nephritis.[2]
Spermatorrhea.[2]
2. Irregular menstruation.[1] Dysmenorrhea.[1]
Leukorrhea.[1] Prolapse of uterus.[1]
Amenorrhea.[1] Uterine bleeding.[1]
Postpartum hemorrhage.[1] Hernia.[1]
Lower abdominal pain.[1] Functional
uterine bleeding.[2] Impotence.[2]
Pelveoperitonitis.[2]
3. Diarrhea.[1] Dysentery.[2]
Round worms in the intestinal tract.[2]
3. Flaccid type of apoplexy.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 3 cun below the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 0.8-1.2 inch. Moxibustion may be applied fairly
long and frequently.[1]
CV 5 Shimen* Front- Mu Point of Sanjiao
INDICATIONS
1. Abnormal uterine bleeding.[1,2]
Leukorhea.[1] Amenorrhea.[1]
Postpartum hemorrhage.[1] Amenorrhea.[2]
2. Retention of urine.[1] Enuresis.[1]
3. Hernia.[2] Abdominal pain.[1]
Diarrhea.[1]
4. Edema.[1]
5. Mastitis.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 2 cun below the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
CV 6 Qihai**
FUNCTIONS: Regulate Qi circulation, tonify Deficient Kidneys, dispel
Dampness.
INDICATIONS
1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Abnormal
uterine bleeding.[1] Leukorrhea.[1]
Postpartum hemorrhage.[1] Enuresis.[1]
Dysmenorrhea.[2] Incontinence.[2]
Polyuria.[2] Urinary retention.[2]
Spermatorrhea.[2] Impotence.[2]
2. Abdominal pain.[1] Hernia.[1]
Diarrhea.[1] Constipation.[1]
Abdominal distention.[2] Intestinal
paralysis.[2]
3. Flaccid type of apoplexy.[1] Neurasthenia.[2]
4. Edema.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 1.5 cun below the umbilicus.
[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-30 mm. Moxibustion may be appled often.[1]
CV 7 Abdomen- Yinjiao*
INDICATIONS
1. Irregular menstruation.[1] Abnormal
uterine bleeding.[1] Leukorrhea.[1]
Pruritus vulvae.[1] Post partum haemorrhage.[1]
Prolapsed uterus.[2]
2. Hernia.[2]Abdominal pain around
the umbilicus.[2]
3. Edema.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 1 cun below the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-30 mm.[1]
CV 8 Shenque**
FUNCTIONS: Warms and stabilizes the Yang, strengthens the transporting
function of the Spleen and Stomach.
INDICATIONS
1. Chronic diarrhea.[1] Borborygmus.[1]
Abdominal pain.[1] Prolapse of rectum.[1]
Acute and chronic enteritis.[2] Intestinal
tuberculosis.[2] Shock resulting from
intestinal adhesions.[2] Prolapsed
anus.[2]
2. Flaccid type of apoplexy.[1]
3. Edema.[2]
LOCATION: In the centre of the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Puncture is contraindicated. Moxibustion is applied with large
cones, 5-15 in number, or with moxa stick for 5-15 min.[1]
CV 9 Shuifen *
INDICATIONS
1. Borborygmus.[1] Abdominal pain.[1]
Ascites.[2] Vomiting.[2]
Diarrhea.[2]
2. Nephritis.[2] Edema.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 1 cun above the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm.[1]
CV 10 Xiawan*
INDICATIONS
1. Gastric pain.[1] Abdominal distention.[1]
Dysentery.[1] Borborygmus.[1]
Vomiting.[1] Undigested food in stool.[1]
Indigestion.[2] Stomach ache.[2]
Prolapsed stomach.[2] Diarrhea.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 2 cun above the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-30 mm.[1]
CV 11 Jianli*
INDICATIONS
1. Gastric pain.[1] Vomiting.[1]
Anorexia.[1] Abdominal distention.[1]
Acute and chronic gastritis.[2] Ascites.[2]
Borborygmus.[2] Abdominal pain.[2]
2. Angina pectoralis.[2]
3. Edema.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 3 cun above the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-30 mm.[1]
CV 12 Zhongwan** Front- Mu Point
of the Stomach
FUNCTIONS: Regulate Stomach Qi, tonify Spleen, relieve retention of
food, eliminate Dampness, subdue ascending Qi of Stomach.
INDICATIONS:
1. Abdominal distention.[1,2] Vomiting.[1,2]
Gastric pain.[1] Regurgitation.[1]
Diarrhea.[1] Dysentery.[1]
Stool with undigested food.[1] Gastritis.[2]
Gastric ulcers.[2] Prolapsed stomach.[2]
Acute intestinal obstruction.[2] Stomach
ache.[2] Diarrhea.[2]
Constipation.[2] Indigestion.[2]
2. Neurasthenia.[2] Mental disease.[2]
3. Hypertension.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 4 cun above the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 25-38 mm.[1]
CV 13 Shangwan**
INDICATIONS
1. Gastric pain.[1] Regurgitation.[1]
Vomiting.[1] Gastritis.[2]
Dilated stomach.[2] Stomach spasms.[2]
2. Seizures.[1]
3. Cardiac spasms.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 5 cun above the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 20-30 mm.[1]
CV 14 Juque ** Front Mu- Point of the Heart
FUNCTIONS: Calm the mind and pacify the Stomach. Much used of epigastric
pain.
INDICATIONS:
1. Pain in the cardiac region and the chest.[1]
Palpitation.[1] Angina pectoralis.[2]
2. Vomiting.[1] Regurgitation.[1]
Difficulty in swallowing.[2] Nausea.[1]
Stomach ache.[2] Hiccough.[2]
3 . Mental disorders.[1] Seizures.[1]
4. Round worms in the bile duct.[2]
Chronic hepatitis.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the abdomen, 6 cun above the umbilicus.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 8-20 mm.[1]
CV 15 Jiuwei* Luo Connecting Point
INDICATIONS
1. Pain in the cardiac region and the chest.[1]
Angina pectoralis.[2]
2 . Mental illness.[1] Seizures.[1]
3. Regurgitation.[1] Hiccough.[2]
4. Asthma. [2]
LOCATION: Below the xyphoid process, 7 cun above the umbilicus. Locate
the point in supine position with arms uplifted.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely downward 13 mm.[1]
CV 16 Zhonting*
INDICATIONS
1. Difficulty in swallowing.[1] Vomiting.[2]
Food stuck in throat.[2]
2. Sensation of fullness in the chest.[1]
3. Asthma.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the sternum, level with the 5th intercostal
space.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
CV 17 Shanzhong** Front- Mu Point of the Pericardium
FUNCTIONS: Regulate Qi circulation, subdue ascending Qi of St, dispel
fullness from chest, soothe diaphragm clear the Lung, resolve phegm.
INDICATIONS
1. Asthma.[1] Bronchial asthma.[2]
Bronchitis.[2]
2. Pain in the chest.[1] Intercostal
neuralgia.[2]
3. Lactation deficiency.[1] Mastitis.[2]
4. Hiccup.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the sternum, between the nipples, level with
the 4th intercostal space.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
CV 18 Yutang*
FUNCTIONS: Facilitates and regulates movement of Lu Qi, cools the
throat and clears the voice.
INDICATIONS
1. Asthma.[1] Cough.[1]
Bronchitis.[2] Emphysema.[2]
2. Vomiting.[2]
3. Intercostal neuralgia.[2]
4. Pain in the chest[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the sternum, level with the 3rd intercostal
space.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
CV 19 Chest-Zigong*
INDICATIONS
1. Asthma.[1] Cough.[1]
Bronchiectasis.[2] Tuberculosis.[2]
2. Pain in the chest.[1]
LOCATION: On the midline of the sternum, level with the 2nd intercostal
space.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
CV 20 Huangai*
INDICATIONS:
1. Asthma.[1,2] Cough.[1]
Bronchitis.[2] Pharyngitis.[2]
2. Pain in the chest.[2] Intercostal
neuralgia.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the sternum, at the level of the 1st intercostal
space.[1]
METHOD:8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
CV 21 Xuanji **
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Bronchial asthma.[2] Chronic bronchitis.[2]
2. Pain in the chest.[1] Cardiac spasm.[2]
3. Spasms of the esophagus.[2]
LOCATION: On the midline of the sternum, midway between Tiantu-
Ren22 and Huagai- Ren20.[1]
METHOD: 8-13 mm horizontally along the skin.[1]
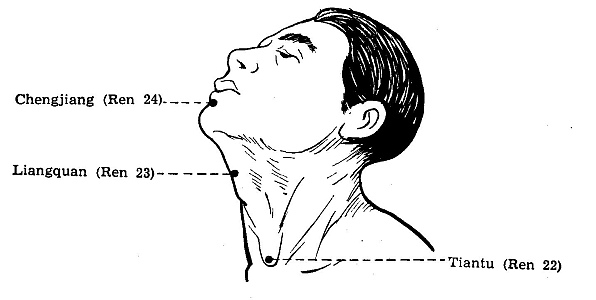
CV 22 Tiantu**
FUNCTIONS Promote dispersing function of Lu, resolve Phlegm, stop
cough,
soothe asthma, clear throat, regulate Qi circulation, dubdue ascending Qi. Ren
INDICATIONS
1. Cough.[1] Asthma.[1]
Sudden hoarseness of voice.[1] Sore
throat.[1] Bronchial asthma.[2]
Bronchitis.[2] Pharyngitis.[2]
Diseases of the vocal chords.[2]
2. Hiccup.[1]
3. Nervous vomiting.[2] Spasms of
the esophagus.[2]
4. Goiter.[2]
LOCATION: In the centre of the suprasternal fossa.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely 13-18 mm towards the posteor inferior aspect of the
sternum. Deep puncture is not advisable.[1]
CV23 Lianquan*
FUNCTIONS: Stiffness of tongue, ease the throat (Wind-stroke) Ren
24-Chengjiang
Dispel Wind. Sedative- to stop pain
INDICATIONS
1. Swelling of the subglossal region.[1]
Paralysis of hypoglossus muscles.[1]
Salivation with glossoplegia.[1] Aphasia
with stiffness of tongue.[1] Sudden
hoarseness of voice.[1] Difficulty
in swallowing.[1]
2. Bronchitis.[2] Pharyngitis.[2]
Tonsillitis.[2] Loss of voice.[2]
LOCATION: Above the Adams apple, in the depression at the upper border
of the hyoid bone.[1]
METHOD: Perpendicular 13-25 mm with the needle directed upward.[1]
CV 24 Chengjiang**
INDICATIONS
1. Facial paralysis.[1] Hemiplegia.[2]
2. Facial swelling.[1] Swelling of
the gums.[1] Excessive salivation.[1]
Ulcers in the mouth.[2]
3 . Toothache.[1]
4 . Mental disorders.[1]
LOCATION: In the depression in the centre of the mentolabial groove.[1]
METHOD: Obliquely upward 5-8 mm.[1]
[2] Acupuncture A comprehensive Text Beijing